Introduction to AI and Digital Twins
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Digital Twins are two transformative technologies that are reshaping and optimising most industry-specific use cases worldwide. The primary key factors are efficiency, innovation, and sustainability, which are mandatory for any industry to face increasing demands and customer bandwidth and retain them. The synergy between AI and Digital Twins is emerging as a GAME-CHANGER, no question about it.
What is a Digital Twin?
Make it simple: "This is a virtual replica of a physical entity,” be it an object, system, or process. This replica is not static; it evolves in real-time, mirroring its physical counterpart by integrating data from sensors and IoT devices.
This enables businesses and organisations to visualise, analyse, and simulate real-world scenarios in a digital environment, empowering them to make informed decisions and optimise operations.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
On the other hand, AI acts as the brain that drives these digital twins. AI is an extrasensory capability capable of processing and analysing the massive amounts of data collected by digital twins, identifying patterns, making predictions, and suggesting actionable insights for multiple use cases.
AI transforms raw data into meaningful intelligence, allowing digital twins to learn, follow up, adapt, and become more effective over time.
Generally, these two entities perform according to individual needs; when both are together, they create a powerful combination, enabling industries to innovate faster, reduce costs, and improve reliability. Many industries benefit from this combination.
This combo (AI and Digital Twins) fuels advancements supporting many industries, such as manufacturing, predictive maintenance, personalised healthcare treatment, disease prediction, Infrastructure aspects of building smart cities, Oil and Gas for sustainable energy, and much more.
AI and Digital Twins pave the way for a more connected, efficient, and intelligent future.
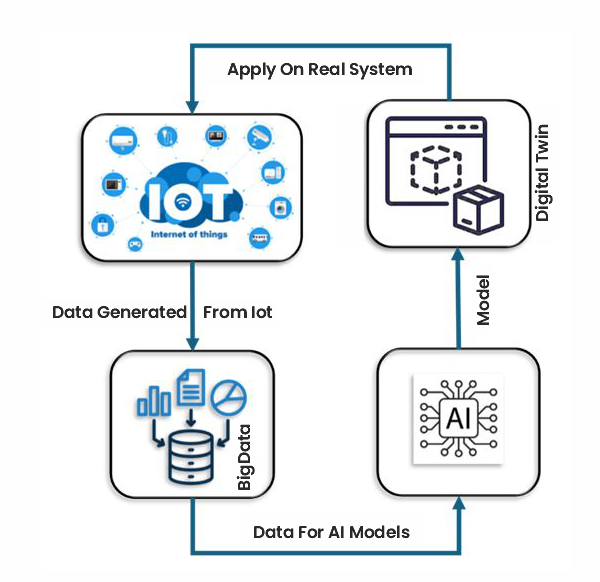
Figure 1: AI and Digital Twins block diagram
Let's discuss the components of AI and Digital Twins implementation, along with their role, technology used, and functionalities.
Key Stages and Components of Digital Twins and AI
The synergy between digital twins and artificial intelligence (AI) is built on a set of essential components that enable these technologies to function effectively and precisely. Each element in the list is critical in creating virtual replicas, analysing data, and driving actionable insights specific to the industry use case.
Below is a list of key components of digital twins and AI:
- Data Acquisition: Using IoT sensors and devices, this collects real-time data from physical assets, systems, or processes. When considering the manufacturing industry, the data is measured through sensors such as temperature, pressure, vibration, and other environmental or operational metrics. The collected data is transmitted to the digital twin as shown in Figure 2, enabling it to reflect the current state of its physical equipment and facilitating accurate analysis and further simulation purposes.
- Role: This helps collect real-time data from physical assets, systems, or processes.
- Key Technologies: We support IoT sensors, embedded systems, and edge devices as key technologies.
- Functionality: These sensors capture the physical parameters like temperature, pressure, vibration, and humidity from the equipment and transmit them to the digital twin for analysis through Big Data and AI systems.
- Digital Model: A digital model is a virtual representation of a physical object, system, or process. It replicates its real-world systems' geometry, behaviour, and performance using engineering tools like 3d modelling and simulation software. With the help of Big Data, AI systems will be continuously updated with real-time data and react accordingly. The digital model evolves to mirror the current state of the physical entity, enabling analysis, prediction, and optimisation with the help of other systems in the block represented in Figure 1.
- Role: Exactly, this is a virtual replica of the physical entity and acts as a twin
- Key Technologies: 3D modelling, CAD (Computer-Aided Design) (Autodesk Revit), MATLAB/Simulink, OpenSimulator, etc..
- Functionality: The model evolves with real-time data to mirror the current state and access the physical environment.
- Data Integration and Processing: Data integration and processing involve consolidating and transforming data from various sources such as sensors, IoT devices, and historical databases. We can observe this in Figure 1, Data from IoT into Big Data Environment. Technologies such as cloud computing, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), ELT, and storage include data lakes and delta lakes. The data pipelines take care of all these demonstrations, which enable the efficient handling of large datasets, ensuring real-time updates and making the data available for the AI block to access. The model generates accurate results and passes them to simulations.
- Role: Consolidate data from multiple sources and build the data that will support the AI models' identification of patterns, predictions, and suggestions of actionable insights.
- Key Technologies: Cloud Computing, ETL/ELT and storage services such as data lakes.
- Functionality: Ensures that data from sensors, historical records, and external systems are seamlessly integrated for analysis and transforming the data for AI systems.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI enhances digital twins by analysing real-time and historical data to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and optimise performance. Using machine learning and advanced analytics, AI enables simulations, fault predictions, and scenario testing, making digital twins smarter and more adaptive over time. This empowers businesses to make informed decisions, reduce downtime, and improve operational efficiency.
- Role: Analyse data, identify patterns, and generate insights, predict outcomes, and optimise performance using Data Science, Machine Learning, Deep Learning and many more techniques.
- Key Technologies:
- Data Science: Analysing the data and understanding the correlations between the features of the dataset and generating insights.
- Machine Learning: For predictive and prescriptive analytics, generating patterns and insights.
- Deep Learning: For complex simulations and decision-making.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): For understanding and generating human-like text.
- Functionality: AI powers the decision-making and predictive capabilities of digital twins, enabling them to simulate scenarios, forecast outcomes, and improve over time. This information is passed on to the digital twins and helps them understand how the real system works.
- Simulation and Analytics: The simulation and analytics stage enables the digital twin to model "what-if" scenarios, predict future outcomes, and optimise system performance. It is the backbone of the entire system. It leverages real-time and historical data, and these components provide insights into operational efficiency, potential risks, and decision-making strategies.
- Role: Test scenarios and find the results from "what-if" analysis, then optimise processes and predict outcomes.
- Key Technologies:
- MATLAB/Simulink: Used for system modelling, simulation, and control design across engineering disciplines.
- Siemens Simcenter: Combines simulation, testing, and analytics for predictive engineering insights.
- Arena Simulation: Focused on process modelling and operational analysis for business systems.
- Functionality: Digital twins use simulation to model "what-if" scenarios, helping organisations prepare for future challenges or optimise operations, and they provide insights into operational efficiency, potential risks, and decision-making strategies.
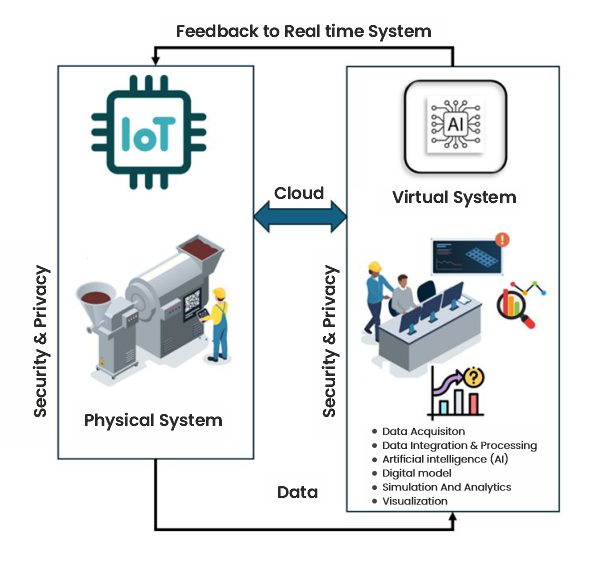
Figure 2: AI and Digital Twins implementation (Manufacturing industry)
- Role: Provide intuitive interfaces for monitoring and interacting with digital twins. Present complex data through dashboards, 3D models, and immersive AR/VR experiences to enable scenario exploration and informed decision-making for stakeholders
- Key Technologies:
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR).
- Dashboards and 3D visualisation tools.
- Functionality: Allow stakeholders to monitor the digital twin, view insights, and explore scenarios interactively.
- Security and Privacy: Data security and privacy are important aspects while building digital twins, and security and privacy have to be ensured in the same way, since the data flowing between physical systems and their digital twins must remain protected from breaches, data leakage, tampering, and unauthorised access. We have to design the system in such a way as to protect it by implementing encryption, secure communication protocols, and robust authentication mechanisms so organisations can safeguard sensitive information, maintain system integrity, and comply with data protection and governance regulations.
- Role:
- Safeguard sensitive data shared between physical and digital entities.
- Prevent unauthorised access and cyberattacks through encryption and secure communication protocols.
- Ensure compliance with data protection regulations and maintain stakeholder trust.
- Key Technologies: Blockchain, encryption protocols, and cybersecurity frameworks. Encryption Protocols
- Data Protection Tools:
- GDPR Compliance Solutions: Tools like TrustArc to ensure compliance with data privacy laws.
- Blockchain: Provides decentralised and tamper-proof data storage for critical applications.
- Edge and Cloud Security
- AWS Shield or Azure Security Centre: For cloud-based security.
- Edge Computing Security Tools: Protect data processed at the edge.
- Data Protection Tools:
- Functionality: Safeguard the integrity of data flowing between physical and digital entities, preventing unauthorised access or tampering. Digital twins’ security and privacy must also be ensured since the data flowing between physical systems and their digital twins must remain protected from breaches, data leakage, tampering, and unauthorised access.
- Role:
Key Transformative Applications Across Industries
Let's explore how digital twins and AI specifically support and enhance performance and functionalities within various industries.
Manufacturing and Smart Factories
Digital twins and AI are reshaping the manufacturing landscape by enabling smart operations, performance, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, real-time decision-making, and efficient resource utilisation. With the help of digital twins and AI, we can create virtual models of machines, manufacturing, optimisation, and production line enhancements in and around entire factories, allowing simulation and predictive insights that improve productivity and reduce operational costs and risks.
Let's discuss a few specific applications.
- Predictive Maintenance: Digital twins of critical machinery continuously collect sensor data and apply AI algorithms to monitor wear and tear. This helps predict potential failures before they happen and schedule maintenance at the right time to increase the lifespan of the machines.
- Benefits: Reduces unexpected downtime, improves asset permanence, and cuts maintenance costs significantly.
- Production Process Optimisation: By simulating the entire production line using digital twins, AI can detect inefficiencies such as delays, underutilised equipment(s), or imbalanced workloads across the production line. Manufacturers can test different processes and configurations without disrupting the production unit and incurring additional expenses.
- Benefits: Enhances throughput, reduces cycle time, manages workload and capacity assessments, and maximises overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
- Quality Control and Defect Detection: Using this technology, AI-enhanced digital twins compare real-time product data against design specifications to identify product defects early in manufacturing. Integrated vision systems and pattern analysis further improve the accuracy and quality of the final product.
- Benefits: Ensures consistent product quality, lowers rework, decreases scrap rates and waste, and reduces customer complaints.
- Factory Layout and Workflow Simulation: Manufacturers can use digital twins to model factory layouts, simulate material flows, and assess human-machine interactions. AI helps optimise the design for space utilisation, enhance safety measures, and improve productivity.
- Benefits: Streamlines factory operations, enhances worker efficiency, and supports lean manufacturing initiatives.
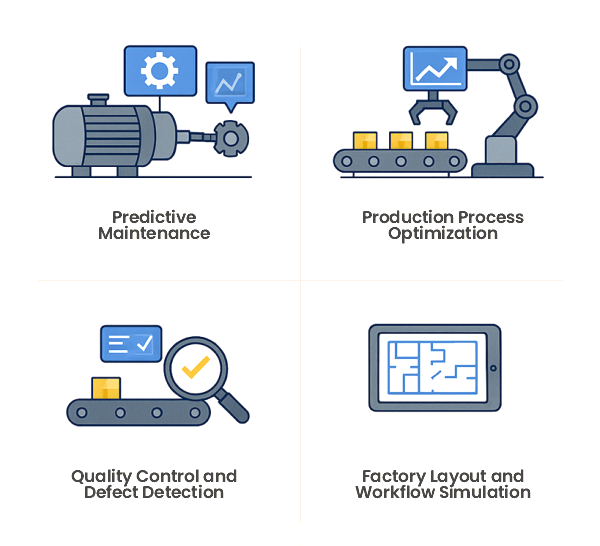
Figure 3: AI and Digital Twins implementation (Manufacturing and Smart Factories)
Challenges and Considerations
Adopting Digital Twins and AI in manufacturing holds great promise, but implementing these technologies has unique challenges requiring careful strategic planning.
- Integration with Legacy Systems and Interoperability: Manufacturing environments typically consist of equipment from multiple equipment manufacturers and vendors, leading to inconsistent data formats and communication protocols based on the equipment configuration. Integrating these diverse systems into a unified digital twin ecosystem is a complex technical challenge, often demanding significant reengineering.
- Consideration: Adopting standard protocols like Open Platform Communications - Unified Architecture(OPC-UA) and scalable middleware solutions can bridge the gap between legacy and modern systems.
- Cybersecurity Risks in Connected Environments: As smart factories rely on real-time data sharing between machines, sensors, and cloud platforms, they become highly vulnerable to cyber threats, including ransomware and system tampering.
- Consideration: Deploying secure edge devices, encryption protocols, network segmentation, and continuous security monitoring is essential for operational safety.
- Data Reliability and Real-Time Performance: Digital twin systems depend on high-quality, accurate, and timely data. Issues like faulty sensors, missing telemetry, or latency can severely impact decision-making, simulations, and predictive accuracy.
- Consideration: Invest in robust sensors, real-time processing pipelines, and automated data validation frameworks to ensure dependable insights.
Healthcare
Integrating digital twins and artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare is revolutionising various aspects such as patient care, medical research, personalised treatment, and operational efficiency. By creating virtual replicas of patients, medical devices, or healthcare facilities, digital twins, powered by AI, offer real-time insights, predictive analytics, and personalised treatment options.
The problem stemmed from how the algorithm measured healthcare needs. It used past healthcare costs as a proxy for health needs and assumed that patients with higher historical costs needed more care. But, due to systemic inequalities that have existed in healthcare access in the US, Black patients typically had lower healthcare costs than white patients with the same conditions.
In healthcare, Digital Twins enable personalised treatment plans and advanced medical research.
This technological growth is helping to build virtual replicas of human organs, created using patient-specific data, allowing doctors to follow exercise:
- Simulate surgeries and predict outcomes.
- Monitor chronic conditions in real-time.
- Customise treatment based on individual responses.
Digital Twins of medical devices and hospital infrastructure also ensure optimal performance and resource allocation.
Let's discuss a few specific applications.
- Personalised Medicine: Digital twins of individual patients simulate their physiological conditions using AI-driven data analysis and predict personalised medicine for patients.
- Benefits: Tailored treatment plans, predicting drug efficacy, and reducing adverse reactions.
- Surgery Simulation and Training: AI-powered digital twins of organs and body parts help simulate surgeries and train medical professionals so that they can better understand the challenges and procedures hands-on before they go for real surgery.
- Benefits: Minimises risks and enhances surgical precision.
- Predictive Diagnostics: AI analyses data from patient-specific digital twins to detect early signs of diseases such as diabetes and cancer.
- Benefits: Enables early intervention and improves treatment outcomes. Provides real-time updates and personalised lifestyle recommendations.
- Drug Development and Clinical Trials: AI-powered digital twins simulate drug effects on virtual populations, which certainly helps to provide drug development and clinical trials with cost and time effectiveness.
- Benefits: Accelerates drug development and reduces reliance on physical trials
- Hospital Management and Optimisation: Not only do digital twins help Personalised Medicine, Surgical Simulation and Training and Predictive Diagnostics in healthcare, but they also facilitate optimising patient flow, resource allocation, and emergency preparedness with the help of technology development
- Benefits: Reduces operational costs and improves service delivery.
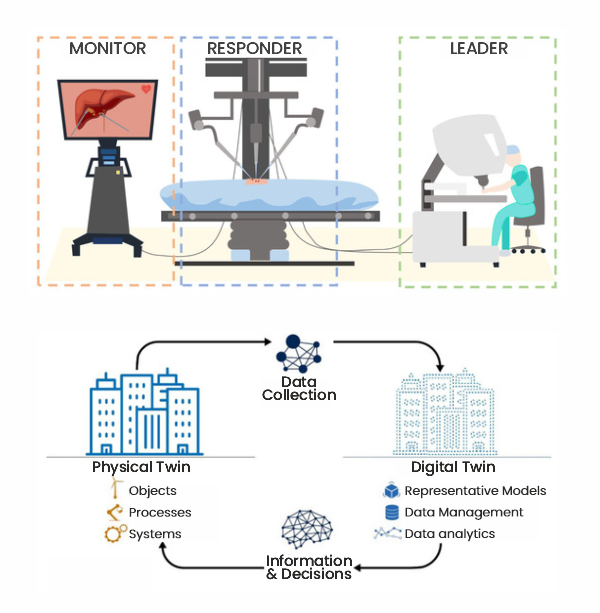
Figure 4: AI and Digital Twins implementation (Healthcare Industry)
(Source: MDPI)
Key Benefits of Digital Twins and AI in Healthcare
We have discussed the classical applications of Digital Twins and AI in the Healthcare industry. Here are the key benefits.
- Patient-Centric Care: Focuses on personalised and preventive healthcare and giving special attention to the patient's health.
- Enhanced Precision: Provides highly accurate insights for diagnosis and treatment with appropriate analysis and predictions.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Enables continuous tracking of patient health metrics and gives patients appropriate treatments on time.
- Improved Efficiency: Highly cost-effective, Streamlines operations and resource utilisation in healthcare facilities, and plans for further expansion through a thought process.
Challenges and Considerations
Integrating Digital Twins and Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare offers revolutionary capabilities from personalised treatment to predictive diagnostics. However, their adoption presents several critical challenges that must be addressed to ensure responsible and effective utilisation.
- Data Privacy and Security: Healthcare data is among the most sensitive forms of personal information. Digital twins rely heavily on real-time patient data, such as clinical records, biometric, and genomic data, to simulate and predict health outcomes. This eventually increases the risk of data breaches, unauthorised access, or misuse of personal information.
- Consideration: Build security frameworks that must be in place, including data encryption, anonymisation techniques, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
- Interoperability Across Healthcare Systems: Clinics, labs, and research centres often use disparate healthcare IT systems and electronic health record (EHR) formats. This division makes it difficult for digital twins to access and synthesise data consistently across platforms.
- Consideration: Adopting Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standards and API-based data integration can improve interoperability. Creating a universal data language for healthcare systems enables digital twins to function accurately and consistently across institutions.
- Ethical Concerns and Algorithmic Bias: AI-driven digital twins are trained on historical datasets that may reflect societal biases. For example, due to under-representation in training data, diagnostic models may fail for certain ethnicities, age groups, or genders. Additionally, it can raise concerns over explainability and accountability.
- Consideration: Healthcare providers must ensure transparency in AI models, conduct bias audits, and develop explainable AI frameworks. Clinical decisions should be AI-assisted, not AI-driven, ensuring the final responsibility remains with trained medical professionals.
Energy and Utilities
The convergence of digital twins and AI is reshaping the energy and utilities sector by improving efficiency, sustainability, and resilience. By creating virtual replicas of physical assets, systems, and processes, AI-powered digital twins enable real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and optimised operations, paving the way for smarter energy management and sustainable utility practices.
Applications in Energy and Utilities
- Grid Optimisation and Stability
- Digital twins of power grids monitor performance in real time and simulate the impact of demand fluctuations. This helps the AI predict outages and optimise load distribution to maintain grid stability.
- Renewable Energy Management
- Wind and solar farms model turbine and panel performance using digital twins. With digital twins and AI, we can drive analytics to predict weather conditions and optimise energy generation.
- Predictive Maintenance
- Digital twins of critical assets such as turbines, transformers and pipelines can be monitored and assessed for their health and safety. It also predicts failures and schedules maintenance, reducing downtime and repair costs.
- Energy Storage and Battery Management
- Digital twin models energy storage systems to optimise charging and discharging cycles regularly, improving battery lifespan and efficiency by predicting usage patterns.
- Water and Wastewater Utilities
- Digital twins and AI enhance wastewater treatment by predicting system overload and improving processing efficiency. This leads to helping water distribution networks detect leaks and optimise water flow.
- Smart Metering and Consumer Energy Management
- Digital twins of consumer systems simulate energy usage patterns based on the data and provide recommendations to reduce consumption and cost, promoting energy efficiency.
- Disaster and Emergency Management
- Digital twins simulate the impact of natural disasters such as hurricanes and earthquakes on utility infrastructure from the perspective of a utility and suggest proactive measures to minimise damage and accelerate recovery.
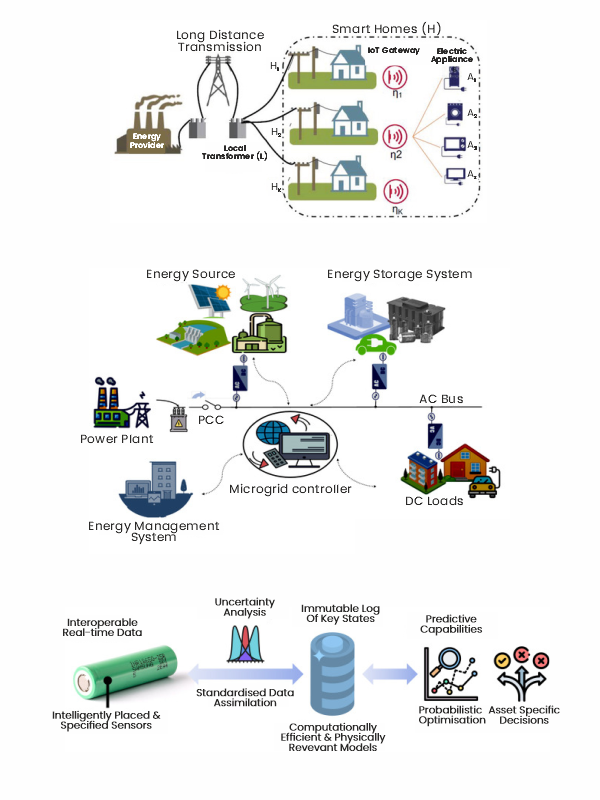
Figure 5: AI and Digital Twins implementation (Energy and Utilities Industry)
(Source: MDPI)
Key Benefits of Digital Twins and AI in Energy and Utilities
We have discussed the classical applications of Digital Twins and AI in the Energy and Utilities industries. Here are the key benefits.
- Improved Efficiency: It optimises asset performance and energy distribution regularly.
- Reduced Costs: Minimise downtime and maintenance expenses through smart metering and consumer energy management
- Proactive Risk Management: This approach mitigates risks from equipment failures or natural disasters and suggests proactive measures to minimise damage and accelerate recovery.
- Customer Empowerment: Enable smarter energy consumption through real-time insights.
Challenges and Considerations
While Digital Twins and AI are revolutionising the energy and utilities sector through smarter operations and predictive analytics, their deployment brings forth several critical challenges that require strategic planning.
- High Initial Implementation Costs: Developing and deploying digital twins in energy systems involves substantial investment in sensors, data infrastructure, simulation software, and AI capabilities. The cost is even higher when scaling across large grids, renewable installations, and critical infrastructure.
- Consideration: Utility providers must evaluate long-term ROI through improved reliability and operational efficiency.
- Data Security and Cyber Threats: Energy infrastructure is a high-value cyberattack target. Digital twins collect, store, and transmit real-time data from critical assets like power grids, substations, and pipelines, making it possible for data breaches or system tampering.
- Consideration: Strong cybersecurity protocols, including data encryption, access controls, network segmentation, and compliance with standards such as ISO 27001, are essential to secure digital twin environments.
- Legacy System Integration: Many energy utilities operate on outdated infrastructure not designed to interface with modern digital twin platforms. Achieving real-time, bidirectional communication between legacy equipment and AI-driven systems is a complex engineering task.
- Consideration: IoT gateways, protocol converters, and middleware can help bridge legacy systems with digital twins. Gradual modernisation with backwards compatibility must be part of the integration strategy.
- Data Quality and Real-Time Reliability: Digital twins in energy systems require high-quality, accurate, and continuous data to perform practical simulations and anomaly detection. Inaccurate sensor readings, delayed data streams, or missing telemetry can degrade model performance.
- Consideration: Regular sensor calibration, redundancy in data collection, real-time data validation, and robust analytics are necessary to ensure consistent data quality.
Conclusion
Digital Twins represent the future of innovation and efficiency, driving transformative change across industries. This technology revolutionises how businesses operate and deliver value by providing real-time insights, predictive capabilities, and enhanced decision-making. As advancements in AI, IoT, and data analytics continue to accelerate, the potential of Digital Twins will only grow, unlocking new opportunities for industries to innovate, optimise, and lead in an increasingly connected world. The future of Digital Twins is not just about mirroring reality; it's about shaping it for a better tomorrow.










